Cytoplasm Variation of mitochondrial
expression in fusion parents and hybrids
The mt types were not only compared at the DNA level
but also at the protein level. Putative differences in the physiology of
distantly related mt types could be relevant for interorganellar compatibility
in somatic hybrids. In order to evaluate the different cytoplasms on their
expression level, in organello translations were performed with
dihaploid potato genotypes with mt genomes a,
b and e.
|
|
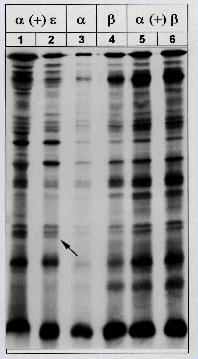
Different mitochondrially
encoded translation products.
On mitochondrial expression level hybrids from an [ a (+) e ] fusion (lane 1,2) could be distinguished by in-organello translation from [ a (+) b ] hybrids (lane 5,6) and dihaploids (lane 3,4). The characteristic additional translation product of 15 kDa deriving from mt type e is marked by an arrowhead. The [ a (+) e ] hybrids differed in their plastid genomes (lane 1:Cp type S, lane 2: Cp type W). This experiment was carried out at the Justus Liebig University in Giessen, and supported by PD. Dr. Renate Horn |
Previous: "3 Levels: DNA -- Expression -- Field "
Abstract of Molecular Analysis
Back to Home Page
Andreas LÖSSL, 10.04.2011