Genetical Distances Between the Main Chondriome Types a, b, g, d, e in Potato For subsequent selection of fusion combinations it was necessary to get an overview about the different phylogenetic branches the main mt types in comparison to the related Solanum wild species. For this purpose the fragment patterns which were generated by the Mt DNA probes were used to perform a cluster analysis and to calculate the relationships of a, b, g, d and e to Solanum wild species. The figure below shows a two dimensional screening, calculated with the model of euclidic distances. - A. Lössl, Cytoplasm Genome Research -
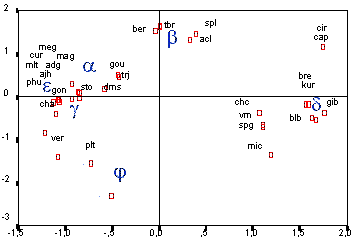
According to dendrogramme and 2-dimensional screen the mt-a and mt-g type were closely related to S. stoloniferum and S. demissum mt genomes. Mt-b is defined as S. tuberosum mt genome. Mt-e is related to S. andigena, goniocalyx, phureja, curtilobum, multidissectum, ajanhuiri and chauca mt genomes.
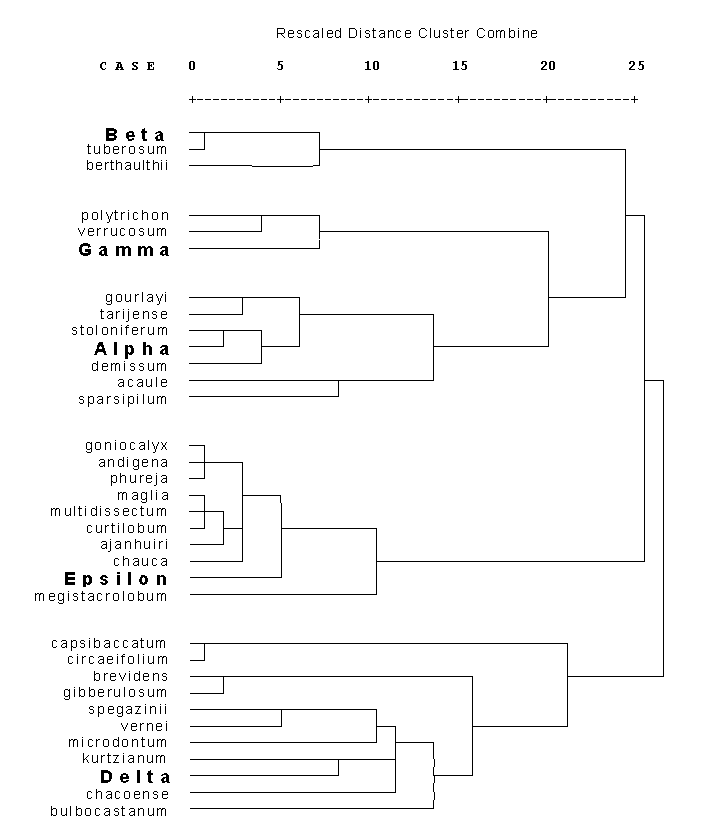
Dendrogram of genetical distances between different Solanum mt DNAs.
The genetical distances were calculated with the model of Euclidic distance. Distances between clusters were calculated by the method ´Average Linkage between Groups´.
RFLP data derive from hybridisation with mt probes containing cob, rps14, rpl5, coxI, rpl2, ccb256, nd3, rps12, atpA, atp6 and orf206.Back to "3 Levels of Differences"
Back to Home Page
Loessl: Cytoplasm Genome ResearchAndreas LÖSSL, 15.10.2010